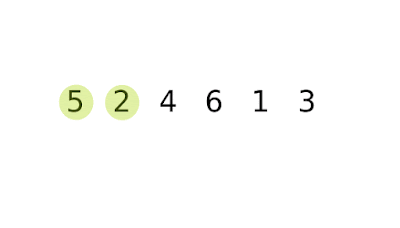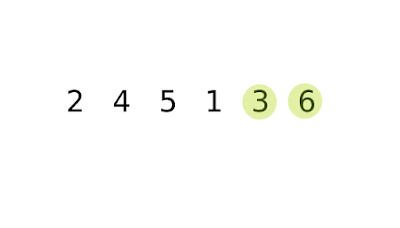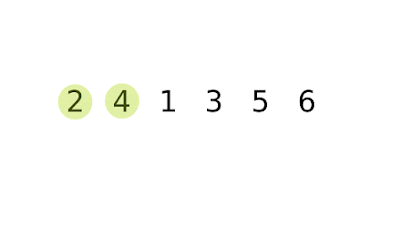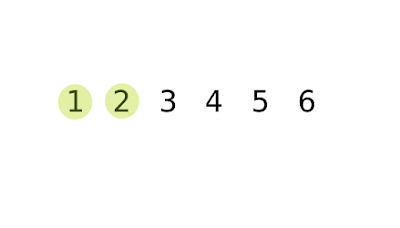 | |
| How Bubble Sort Works |
Bubble Sort OR Sinking Sort
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm. In this algorithm same process happens until the considering list become a sorted list. Throughout the sorting process compares each pair of adjacent items and adjust them one pair at a time.
Lets consider a list containing numbers to be sort
2,4,1,3,5,6
1. lets take first two numbers 2 & 4
2 < 4
2. because of that we don't have to adjust first pair but,
4 > 1
3. because of that we have to adjust 4 & 1
new list : 2,1,4,3,5,6
4 > 3
new list : 2,1,3,4,5,6
4. like this continue until the lat pair
2,1,3,4,5,6
5. after comparing last pair start same process from the beginning of the new list
2 > 1
new list : 1,2,3,4,5,6
6. after this step list becomes sorted.
Pseudo Code Implementation
begin Bubblesort(list)
temp == 0
for all
if list[i] > list[i+1]
temp == list [i+1]
list[i+1] == list[i]
list[i] = temp
end if
end for
return list
end Bubblesort
Python Implementation
def bubbleSort(alist):
for passnum in range(len(alist)-1,0,-1):
for i in range(passnum):
if alist[i]>alist[i+1]:
temp = alist[i]
alist[i] = alist[i+1]
alist[i+1] = temp
Implementation Using C
#include <stdio.h>
void bubble_sort(long [ ], long);
int main()
{
long array[100], n, c, d, swap;
printf("Enter number of elements\n");
scanf("%ld", &n);
printf("Enter %ld integers\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%ld", &array[c]);
bubble_sort(array, n);
printf("Sorted list in ascending order:\n");
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
printf("%ld\n", array[c]);
return 0;
}
void bubble_sort(long list[], long n)
{
long c, d, t;
for (c = 0 ; c < ( n - 1 ); c++)
{
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++)
{
if (list[d] > list[d+1])
{
/* Swapping */
t = list[d];
list[d] = list[d+1];
list[d+1] = t;
}
}
}
}
Time Complexity
- worst case: O( n2)
- best case : O( n)



0 Comments
Thanks for the feedback